Wireless LAN
Begriffe
- BSA: Basic Service Area: Der Bereich den ein AP (physikalisch) abdeckt bzw. abdecken kann
- DS: Distribution System - Anbindung des AP zur restlichen Infrastruktur (Switch, WLC)
- BSS Basic Service Set: AP centralizes access and control over a group of wireless devices
- Architektonische Platzierung in der Topologie
- ESS Extended Service Set - Mehrere Access Points welche ggf. ein und das selbe WLAN ausstrahlen für bspw. Roaming
- BSSID: BSS are identified by their BSSID which is based on their MAC
- Layer 2 MAC Adresse um den Service Set zu identifizieren
- Können mehrere BSSIDs haben; die unterschiedlichen BSSIDs haben dann unterschiedliche MACs
- SSID: Textual name of the BSS/BSSID
- ESSID Textual name of the ESS
- Beacons: AP Broadcasts their information about SSID and authentication requirements with beacon frames
- Can be disabled
- Hidden SSID?
- Roaming: Wireless can roam to other APs supporting the same WLAN when moving around in the building
- Authentication is done by the WLC
- Probe Requests: Devices that activley discover SSIDs are sending probe request frames
- By answering with probe responses that contain beacon information
- Association request: In order to connect to an AP, the device has to send association requests
- The AP grant or deny the request by sending an association response
Wireless Security
Authentication
Open Authentication
- Jeder Client kann sich Authentifizieren - No questions asked!
- NOT Secure
- Wird meist in Kombination mit bspw. Captive Portals genutzt wo sich noch Benutzer anmelden/authentifizieren muss
WEP - Wired Equivalent Privacy
- Authentication und Encryption
- Für Encryption RC4 Algorithmus
- Shared-Key - Sender und Empfänger benutzten für die Ver- und Entschlüsselung selben Key
- Keys von 64bit oder 128bit
- NOT SECURE
EAP - Extensible Authentication Protocol
- EAP ist eigentlich kein Protokoll aber ein Framework für sichere Protokolle
- Definiert einen Satz an Authentication Funktionen
- Integriert sich mit 802.1x (port based access control)
- 802.1x wird zur Authentifizierung genutzt
LEAP - Lightweight EAP
- Username und Passwort für Authentication genutzt
- Beide Parteien tauschen Challenge Messages aus die von den jeweils anderen verschlüsselt zurückgesendet werden
- Nutzt dabei dynamische WEP Keys und gilt daher als nicht sicher
EAP-Fast (Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling)
- Entwickelt von Cisco
- Authentication Credentials werden durch PAC - protected access credential - geschützt
- Phasen
-
- PAC wird erstellt und auf den Client installiert
-
- TLS Tunnel wird gebaut, nachdem Supplicant und AS sich gegenseitig authentifiziert
-
- End User can be authenticated through that Tunnel
-
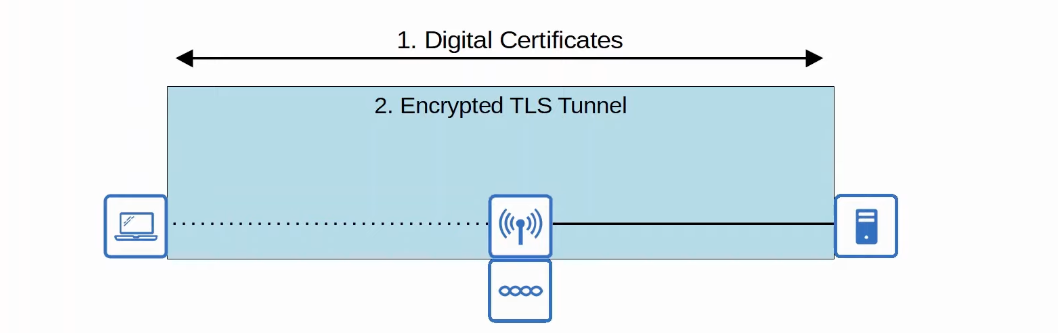
PEAP - Protected EAP
- Funktioniert genauso wie EAP Fast, nur wird zu Authentifizierung des Servers ein Zertifikat vom AS genutzt
- Zertifikat wird auch zum Aufbau des TLS Tunnels genutzt
EAP-TLS
- Ähnlich zu PEAP aber für die Authentifizierung benötigt sowohl der AS als auch der Client ein Zertifikat
- Tunnel wird nicht mehr für Authentifizierung benötigt, darüber werden aber Verschlüsselungsoptionen ausgetauscht
Verschlüsselung
TKIP - Temporal Key Integrity Protokoll
- TKIP wurde entwickelt als WEP nicht mehr sicher war
- Zwischenlösung!
- Wird in WPA genutzt
CCMP
- Genutzt in WPA2
- Muss von Hardware unterstützt werden!
- Nutzt AES für Verschlüsselung in Counter Mode
- Nutzt CBD-MAC für MIC und schützt Integrität
GCMP
- Sicherer und Effizienter als CCMP
- Genutzt in WPA3
- AES Counter Mode für Verschlüsselung
- GMAC für MIC und Integrität
WPA
- Alle WPA Versionen unterstützen Personal Mode und Enterprise Mode
- Personal Mode: Nutzt einen pre-shared key PSK für Authentication - bspw. Password
- PSK will not be send over the air; 4 Way Handshake für Authentication
- PSK wird genutzt um encryption keys zu erstellen
- Enterprise Mode: 802.1X wird für Authentication genutzt (RADIUS Server)
- Alle EAP Methoden sind unterstützt
- Personal Mode: Nutzt einen pre-shared key PSK für Authentication - bspw. Password
WPA 3
- WPA3 schützt die Management Frames from eavesdropping/forging
- SAE: 4way Handshake when using personal mode
- Forward secrecy: Prevents data from being decrypted after it has been transmitted over the air
Wireless LAN Controller (WLC)
- Central point of management
- Monitor WLAN quality, controls channels (bspw. non competing channels) and power of APs
- Can detect rogue APs
WLC Hardware / Interfaces
Der WLC benutzt ein wenig andere Bezeichnungen für seine Interfaces, besonders da auch zwischen physikalischen und logischen Unterschieden wird.
- Redundancy Port
- Der Redundancy Port ist für High Availability Konfigurationen vorgesehen, worin zwei WLCs miteinander verbunden werden.
- Service Port
- Der Service Port ist ein Out-of-band Management Port für Maintenance und System Recovery
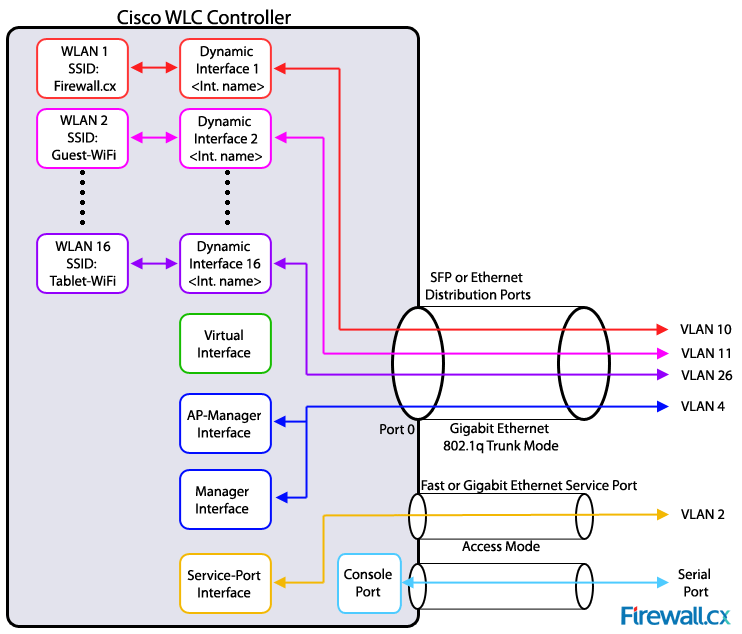
- Distribution System Ports
- “Switch” Ports des WLC welche zu den internen logischen Interfaces (Dynamic Interfaces) angebunden werden.
- Supports also Link Aggregation
- Dynamic Interfaces
- Dynamic Interfaces are logical Interfaces which are mapped to WIFI SSIDs. Think of VLAN interfaces for each SSIDs
- The number of dynamic interfaces and therefore number of possible wifis are depended on the WLC model.
- All dynamic interfaces can be assigned to one physical distribution port, which makes the distribution port a trunk, because of multiple VLANs.
- One Dynamic interfaces can be assigned to one physical interface
- Management Interface
- Another logical interfaces used for managing the WLC itself by administrators
- Also used from the WLC to manage the APs
- AP-Manager Interface
- Layer 3 Communication between lightweight AP and WLC
- IP address is used for the CAPWAP tunnel (Src/Dst IP)
- Interface is optional and depends on the model if you have a physical one
- Setting “Enable dynamic AP Management” to use the Management Interface also as a AP-Manager Interface
Architekturen / Modus
Autonomos AP Architecture
- Standalone werden einzeln gemanaged
Cloud-based architecture
- Bspw. Meraki
- Zentrale Cloud based Management Plattform
- Architektur ist aber gleich zu der Autonomous Architektur
- APs in Cloud-based sind auch Autonomous
- Cloud-based ** ** zu der Data Plane
- Traffic wandert also nicht erst in die Cloud und dann wieder zurück
Ad Hoc
- IBSS: Independent Basic Service Set
- Unabhängig von einem AP
WiFi Direct
Infrastructure Mode
- Infrastructure Mode: Kommunikation mit anderen Geräten durch einen Access Point (kein Wi-fi direct oder AdHoc)
- Wireless ist immer half-duplex- sie sind also vergleichbar mit Hubs
Zero Trust Provisioning
- Erleichtert das Managen und Deployment von Access Points
- Lightweight AP support Zero Touch
- Erkennt seinen WLC durch DHCP, DNS („cisco-capwap-controller“) oder local subnet broadcast
Cisco AP Modes
- Welcher Modus (Autonomus vs Lightweight) genutzt wird, hängt vom installiertem Image auf dem AP ab
Lightweight Mode (Zero Touch Deployment)
- Konfiguration wird vom WLC heruntergeladen
- Das beinhaltet welches WLAN und Einstellungen am AP angeboten werden
- WLC wird dabei zwingend benötigt
Split MAC
- Bestimmte Workloads sind vom AP ausgelagert auf dem WLC
- Real-Time Traffic wird immer noch vom AP bearbeitet, weil der Traffic Delay empfindlich ist
- AP Operations
- Client Handshake on Connecting
- Beacons
- Performance Monitoring
- Encryption and Decryption
- Clients in power save
- WLC Operations
- Authentication
- Roaming Control
- 802.11 to 802.3 communication
- Radio frequency management
- security management
- QoS Management
- Local Mode (Managed)
- Traffic geht getunnelt zum WLC und von dort aus gehen die VLANs aus
- Modellierung von 802.3 (Ethernet) zu 802.11 (WLAN) macht der WLC
- FlexConnect (Managed) ist am AP die Bridge und die eigentlichen Access Ports, die VLANs brechen dort aus
- Traffic is forwarded locally
- Benötigt ein native VLAN untagged, weil er keine Start Up Config hat und daher den WLC über CAPWAP erreichen muss
- FlexConnect encapsuliert nicht über CAPWAP
- Autonomous = Standalone (Unmanaged/Managed individually)
- Zum Access Port muss ein Trunk konfiguriert werden, dann lokal (auf dem AP) das Bridging statt finden kann
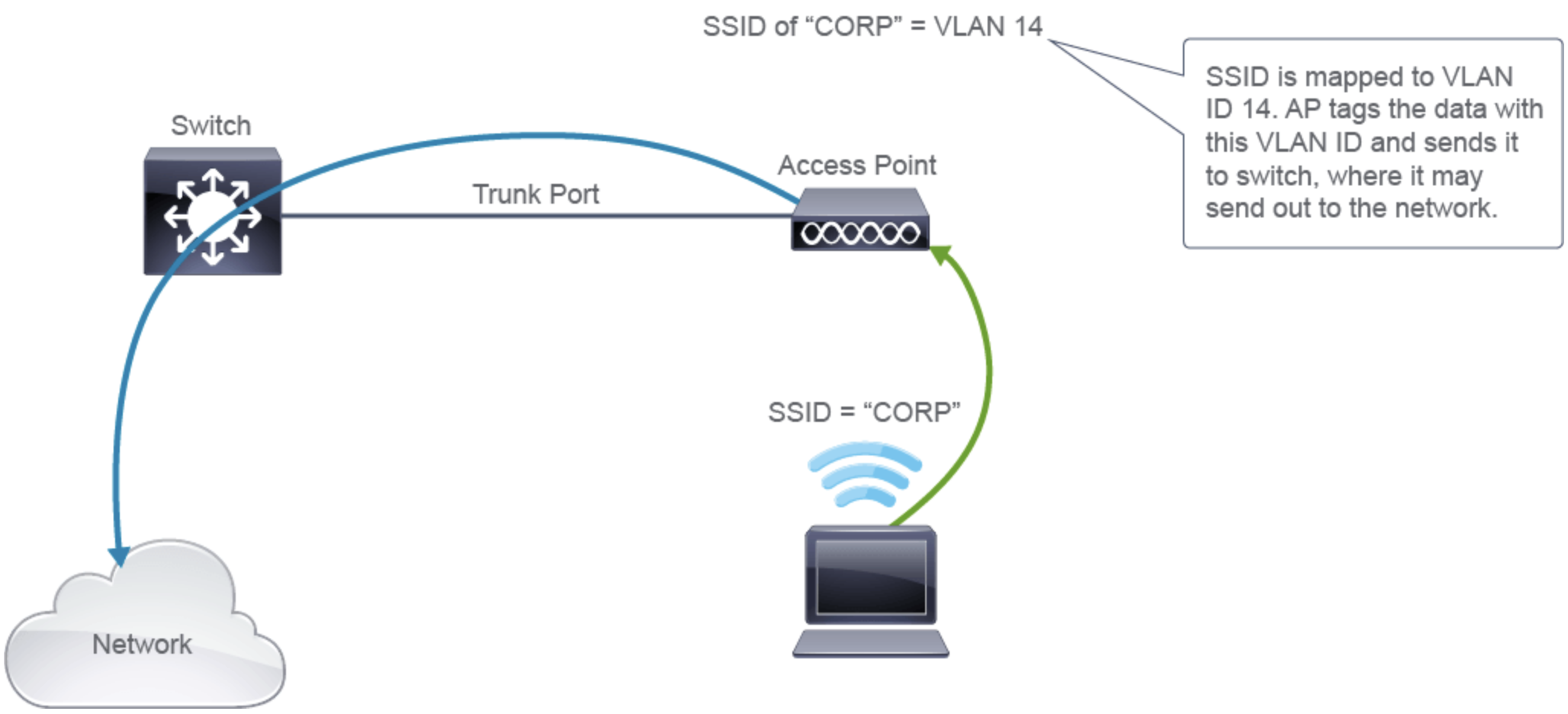
- AP braucht bei Standalone oder FlexConnect einen Trunk mit allen VLANs die lokal gebridged werden soll
- Standalone benötigt kein WLC fürs Managment
- AP tagged den Traffic und leitet ihn zum Switch weiter
CAPWAP Communication
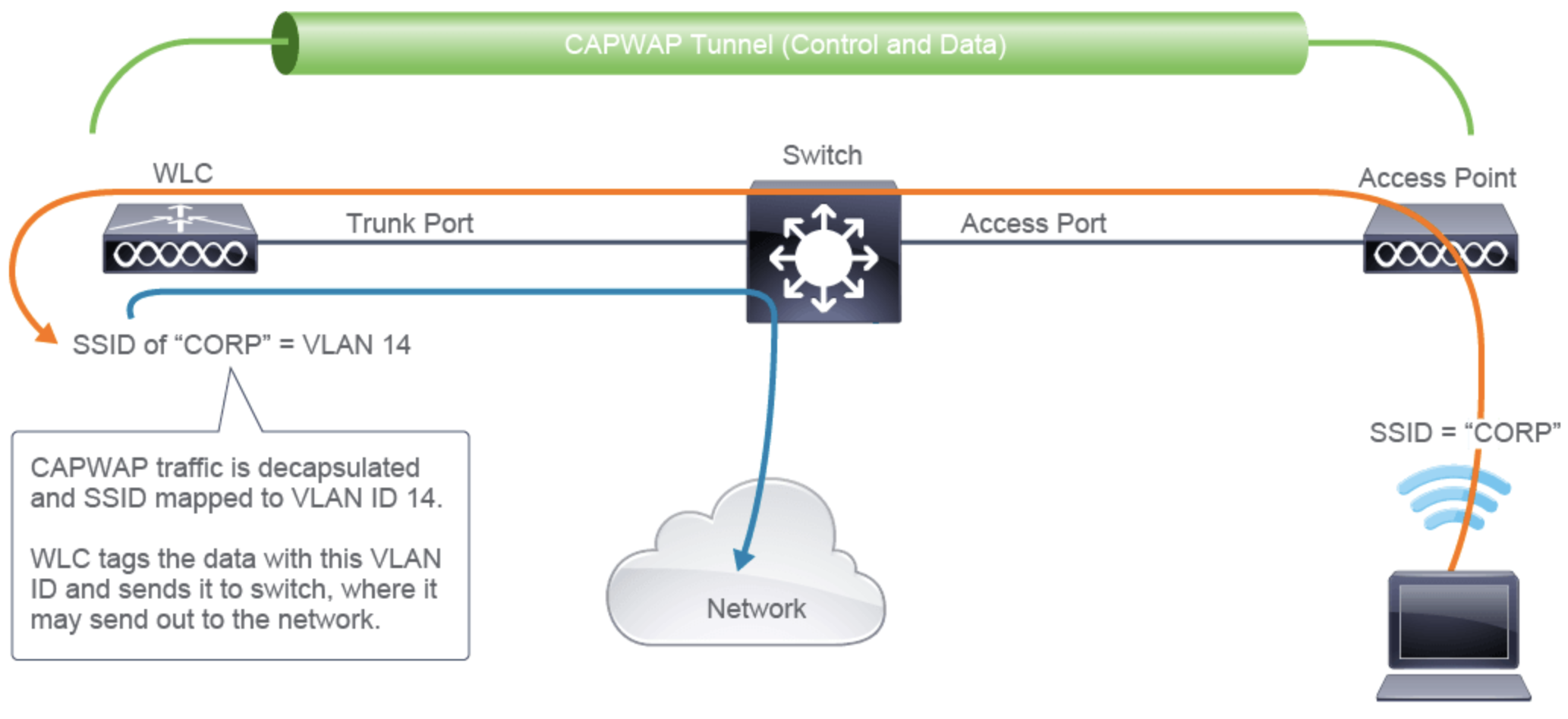
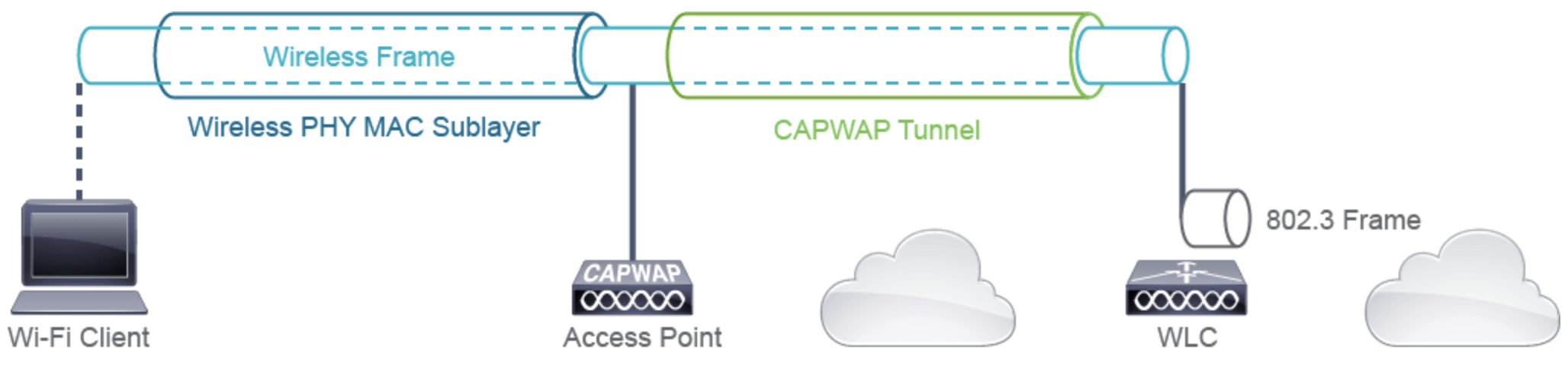
- Control and provisioning of Wireless Access Points (CAPWAP)
- Kommunikation ist verschlüsselt in einem DTLS CAPWAP Tunnel (UDP 5246 u. 5247)
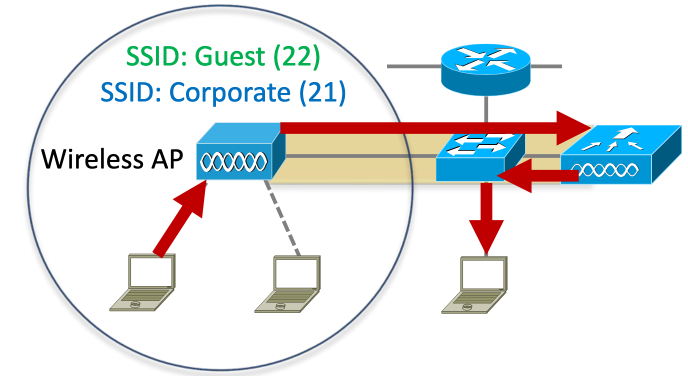
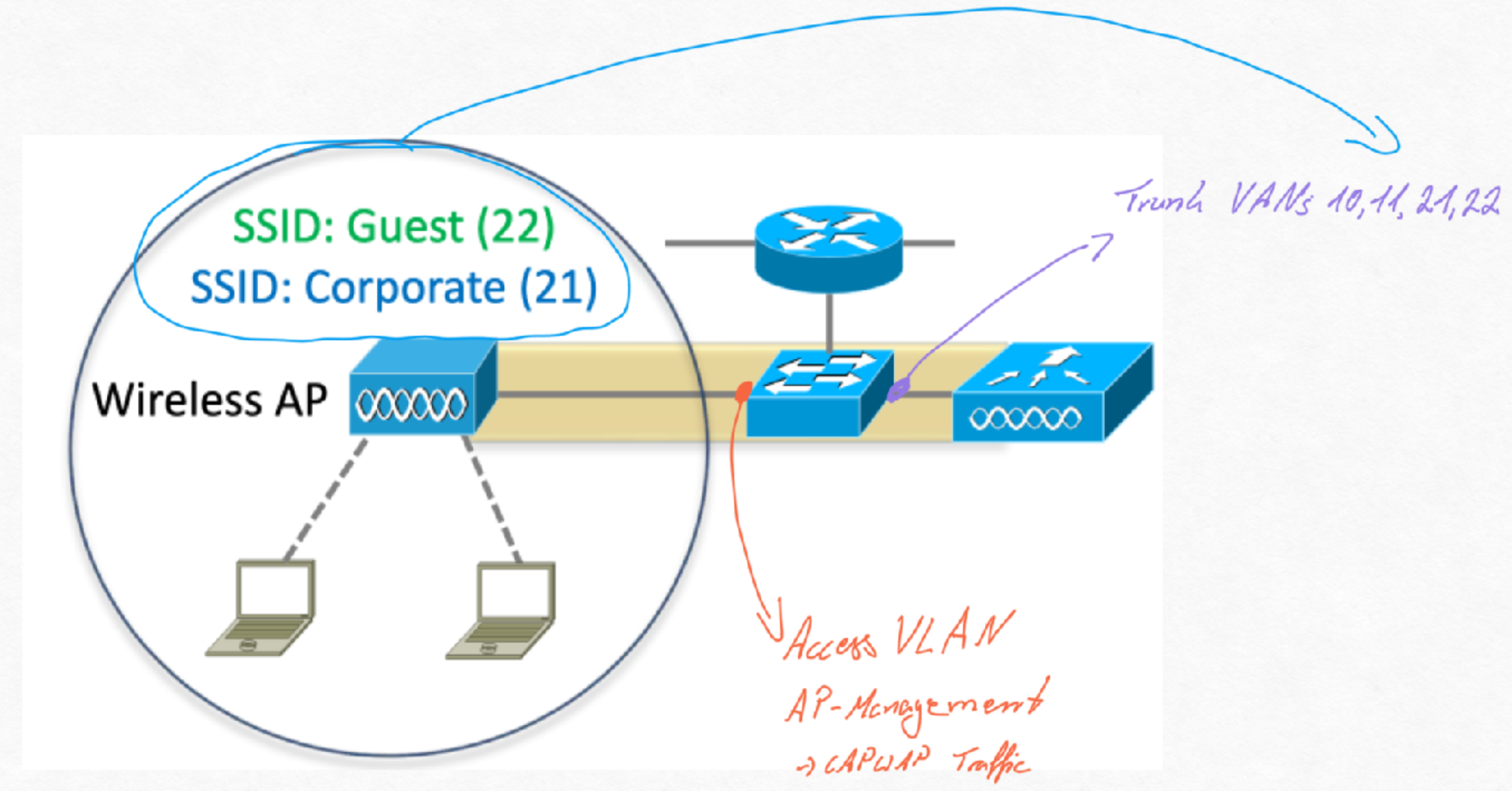
- Für die verschiedenen VLANs werden verschiedene SSIDs benötigt, die VLAN zugehörigkeit wird den assiziationen der gräte/wlans zugeordnet
- Stelle dir den AP als wireless switch vor mit den verschiedenen Access Ports
- Oft wird Etherchannel zusammen mit WLC genutzt
Konfiguration Lightweight
- Zunächst werden alle VLANs benötigt die auf dem AP zur Verfügung stehen soll
- Darüber hinaus benötigt man ein VLAN für das WLC Management indem der Admin den WLC verwaltet und ein AP-Manangement VLAN in dem der WLC die APs verwaltet
- Das AP-Management VLAN hat den CAPWAP Traffic
- Switch Port zum Access Point muss ein Access Port sein mit einem einzigem VLAN
- Workgroup Bridges
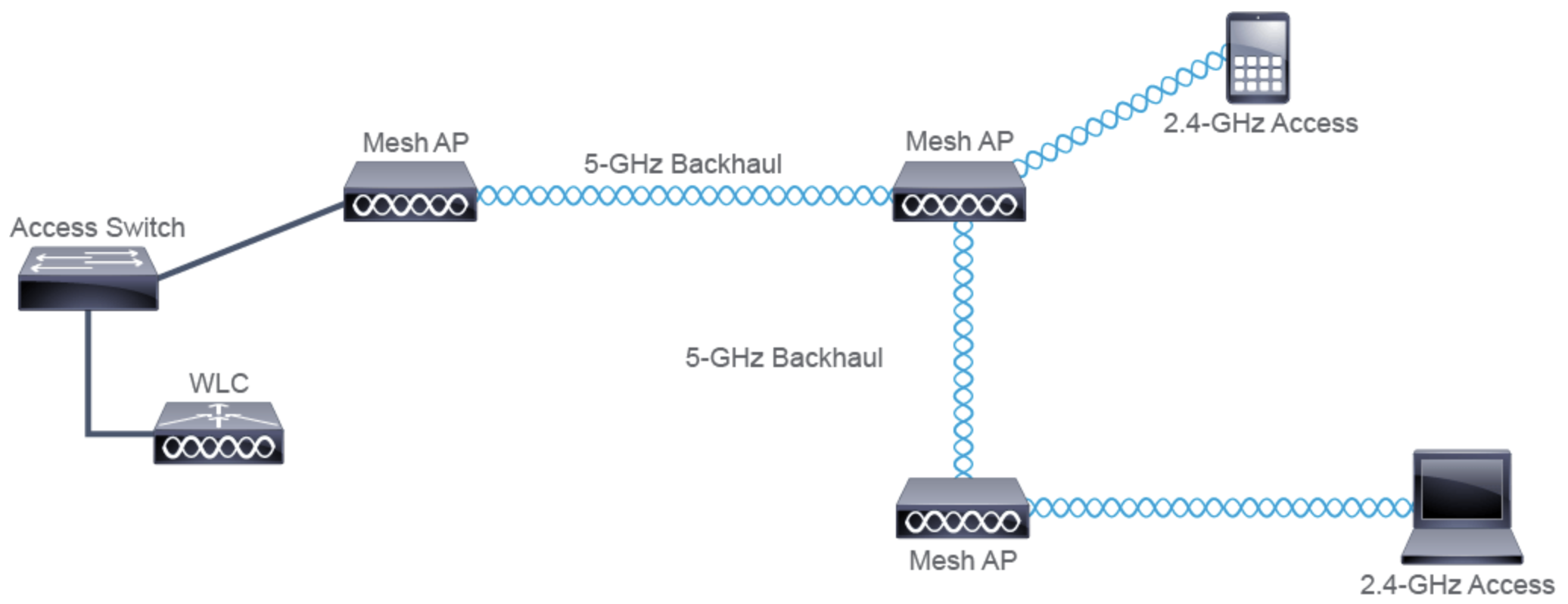
- Mesh
- Ersetzt den DS
- Connection über andere Mesh AP
- Selbstorganisierendes Netz
- Benötigt nur Strom